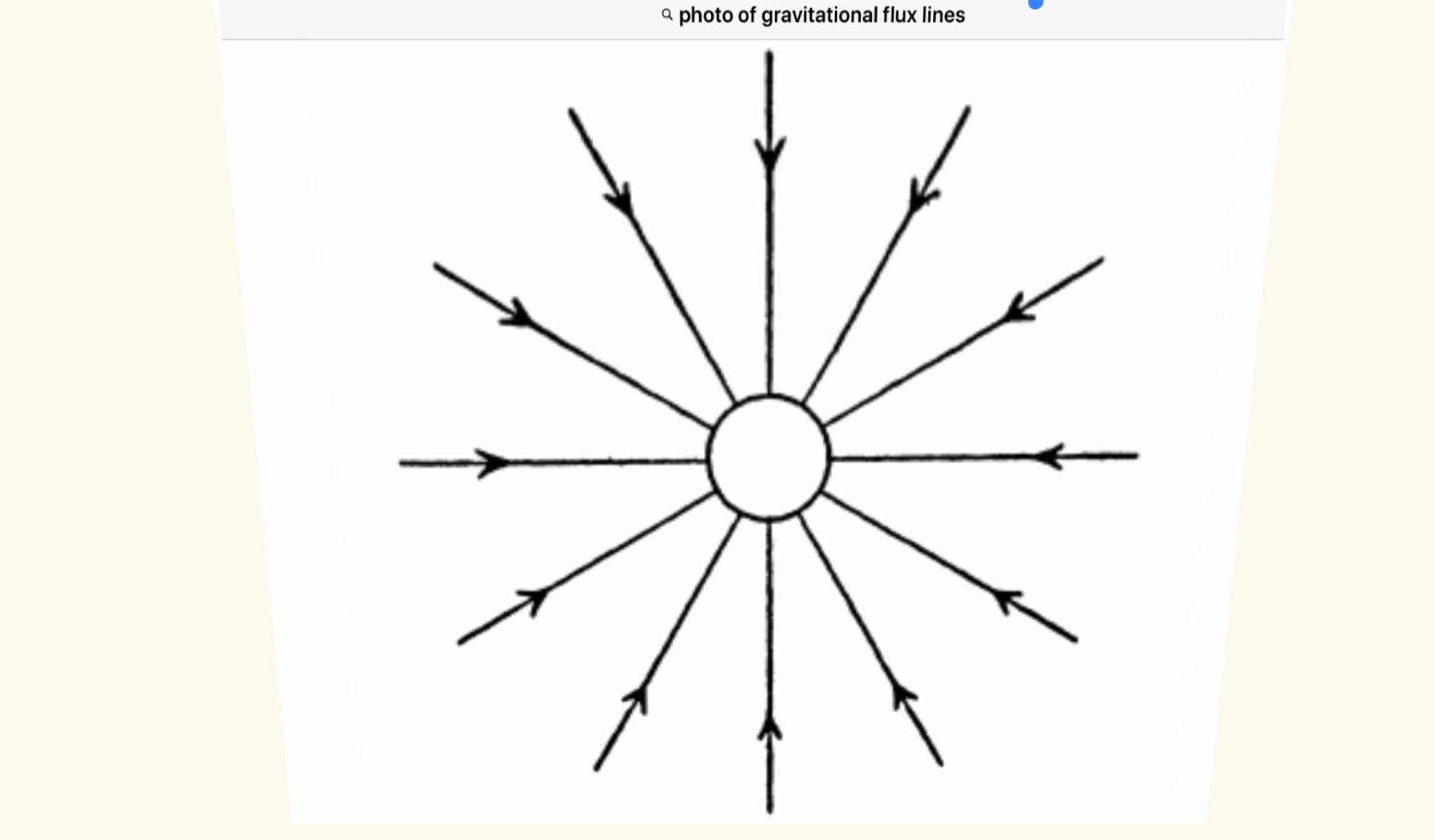
9 8 Gravity Math
G g me r2.
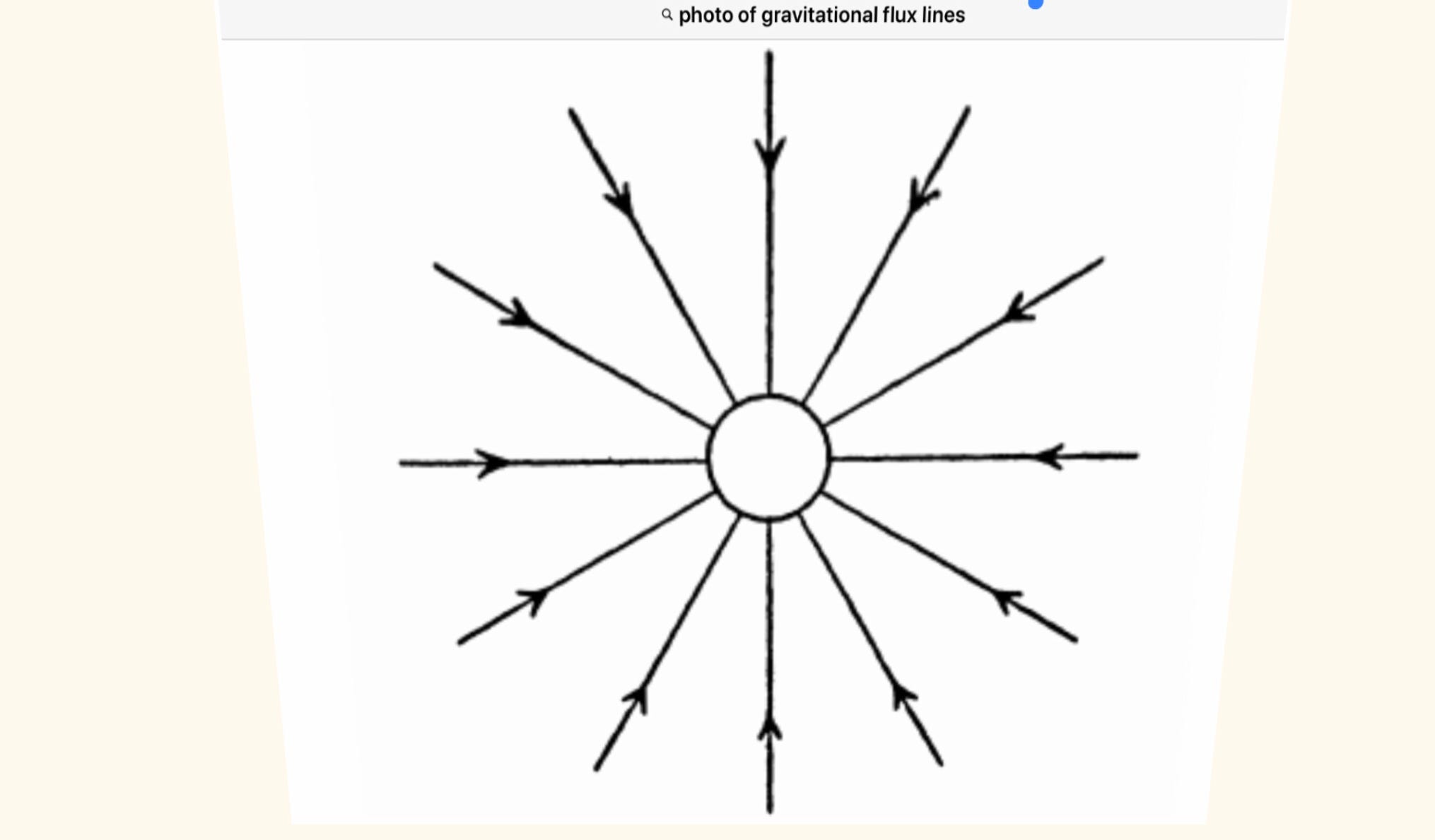
9 8 gravity math. H 1 2gt2 m. 9 8 m s2 is the acceleration due to gravity near the earth s surface. Over time scientists were able to put a value on the acceleration due to earth s gravity as 9 81 m s 2. Free fall means that an object is falling freely with no forces acting upon it except gravity a defined constant g 9 8 m s 2.
This is equivalent to its mass times the force of gravity g a defined constant of 9 8 m s 2 times the height of the object. Galileo observed that all objects fall at the same rate of speed regardless of the object s mass. An object dropped near earth s surface will accelerate downwards at about 9 8 m s 2 due to the force of gravity regardless of size if air resistance is minimal. Mathematically the equation for g is.
G 9 8 m s 2. Since a large object will feel a large force of gravity and a small object will feel a small force of gravity we can t really talk about the force of gravity being a constant. The acceleration due to gravity g was derived from observations of falling objects. The distance the object falls or height h is 1 2 gravity x the square of the time falling.
Velocity is defined as gravity x time. Potential energy mass x gravity x height.