Definition Of Solstice Math
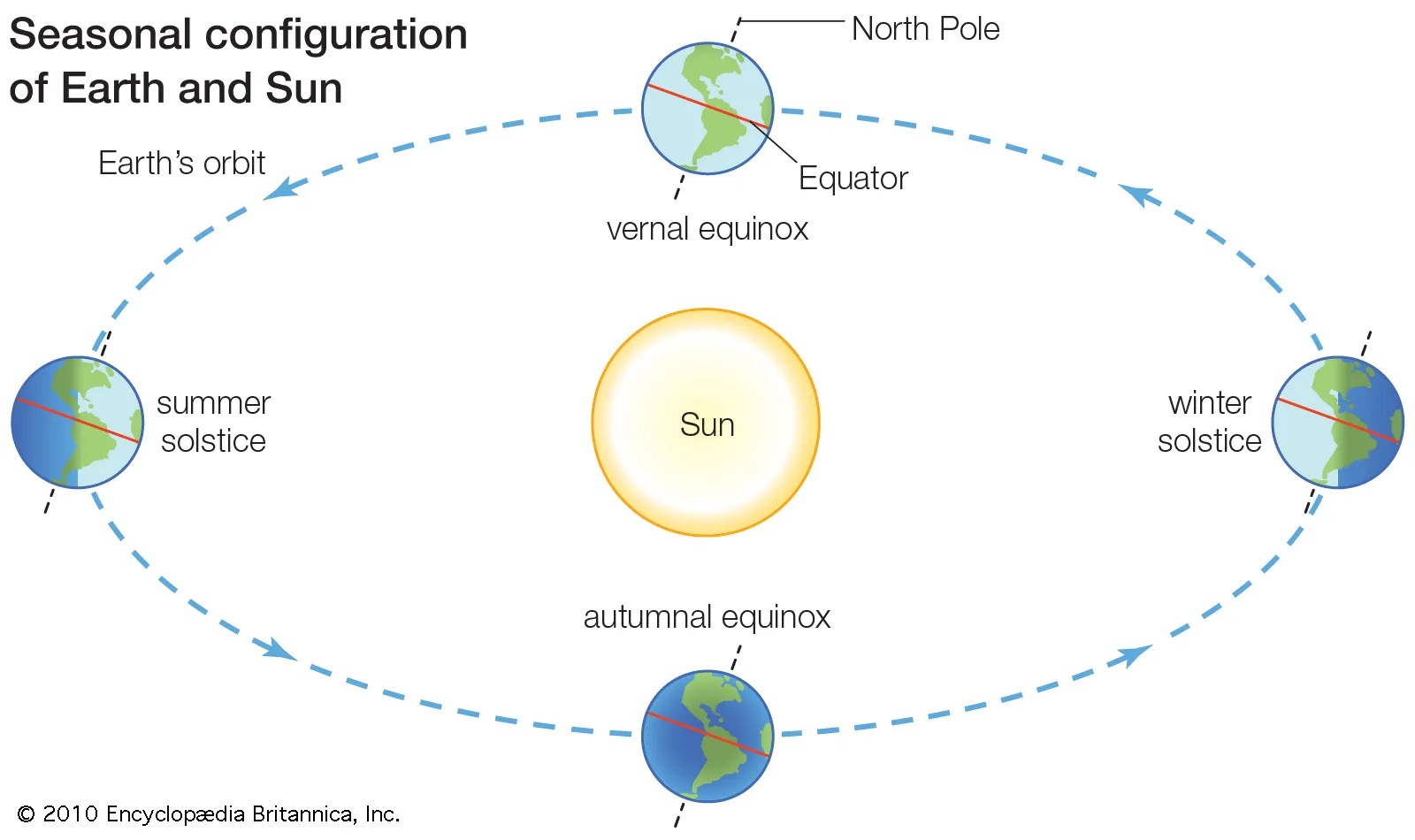
A solstice is a moment in the year when the sun s apparent path is farthest north or south from earth s equator.

Definition of solstice math. The situation is exactly the opposite in the southern hemisphere. The summer solstice occurs when the earth is tilted to be closest to the sun. Not to scale or speed. The solstice combining the latin words sol for sun and sistere for to stand still is the point where the sun appears to reach either its highest or lowest point in the sky for the year and thus ancient astronomers came to know the day as one where the sun appeared to stand still.
Definitions and frames of reference. The days when this happens are called. Solstice happens around june 21 and around december 21 each year. The position of the sun in the sky determines the size of your shadow and also the solstice.
And it loks like this when viewed at 0. Solstice when the earth is the most tilted away or towards the sun. Similarly for an observer on the south pole the sun reaches the highest position on the december solstice day when it is the summer solstice at one pole it is the winter solstice on the other. For an observer on the north pole the sun reaches the highest position in the sky once a year in june the day this occurs is called the june solstice day.
Look it up now. At the solstice the tilt of earth toward the sun is at a maximum angle in one hemisphere and a minimum angle in the other. Solstice either of the two moments in the year when the sun s apparent path is farthest north or south from earth s equator. Summer solstice the longest daytime of the year.
A solstice is a day on which the earth is tilted furthest away from the sun or closest to the sun. Solstice is a science term for two special times a year when the sun is at its highest and lowest. It is the longest day of the year and occurs on around the 21st of december in the southern hemisphere. The earth spins at a 23 5 angle.
See this animation for why it happens.